Each of our wrists has two surfaces that fit together like a lock key. All the bumps on one joint surface correspond to the depressions on the other. Such an exact coincidence of surfaces has a medical name - congruence. From above, the ends of the bones that make up the joint are covered with cartilage for better gliding. The joint bag, ligaments and muscles protect the joint. During arthrosis, one of the most common diseases of the joints is the destruction of cartilage and bone surfaces. At the same time, little is produced by a special joint fluid that ensures smooth movements, the ends of the bones come into contact and begin to rub against each other, causing pain and discomfort to the owner. Meanwhile, in arthrosis, there is formally no inflammation in the joint, which distinguishes it from arthritis.
Why hip arthrosis occurs: age

A catastrophe like arthrosis can happen to any joint in our body. Defeat is one-sided and two-sided. Age, overweight, injuries, flat feet, scoliosis, arthritis, joint displacement, overwork, but a sedentary lifestyle contribute to the onset of the disease. The joints are designed to move! Meanwhile, the vertical posture predisposes to arthrosis of the human hip joint. Such diseases do not occur in animals, and the load on the joints is more evenly distributed.
The hip joint is second after the shoulder joint in terms of range of motion. And indeed, we can normally move our legs back and forth, out and in, and even with rotating movements. This bond carries a very heavy load. It consists of the head of the femur and a socket on the pelvis. Osteoarthritis of this joint is medically called coxarthrosis. A lot of people suffer from this disease. Women are more likely to be ill and, of course, the culmination of the disease occurs after the age of 40 years. In 70% of cases, this is due to natural wear and tear on the joint, damage to the blood supply and metabolism.
Signs of joint damage: pain while walking and at rest

The first symptom of hip arthrosis is lumbar pain when climbing stairs. There may be no pain when you go down the stairs. Later, the pain may begin to spread to the knee. Some of the various movements in the joint will be limited. For example, lifting the leg, that is, bending it at the hip, can be painful, but not taking back the leg. Turning the foot inward is painful, moving it to the side is also painful but tolerable. It is often not possible to kneel, as this movement also affects the hip joint. And restrictions on mobility arise not only from pain, but also from changes in the joint itself.
Given that the hip joint is involved in walking, running, and a host of other movements, its defeat imposes social restrictions on the patient. And in third-degree arthrosis, the pain is disturbing not only during exercise but also at rest, especially not allowing you to sleep at night. It's hard to turn around in bed. And sometimes the pain is so severe that it forces the patient to take a painkiller all the time, which in itself is not always harmless. Thus, frequent use of NSAIDs may lead to the development or worsening of gastric ulcer.
Treatment of arthrosis: joint surgery
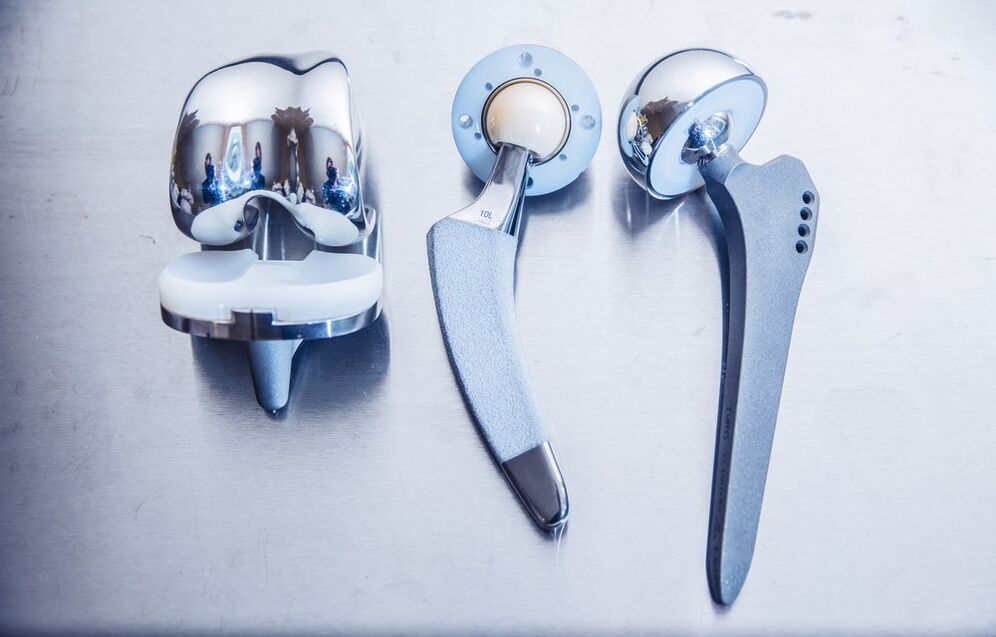

Many years ago, when modern prosthetic surgeries were not yet available, surgeons still operated on patients with coxarthrosis. However, the goal of the surgery was not to treat arthrosis but to completely immobilize the joint. After the patient recovered from this difficult surgery, he walked, pulling his leg. Many movements were out of reach for him, but at least he was not in pain. Then an artificial hip joint was invented and it became possible for such patients to be fully assisted - they could walk with a new joint painlessly and perform other movements no different from healthy people. So an 80-year-old patient underwent joint surgery in both hips and then turned to the doctor with the question, "Can I go skiing? ".
Today, coxarthrosis surgeries are a proven production. Such treatment for hip arthrosis is available to many people, including the very elderly, unless there is, of course, a lifetime contraindication, such as severe heart, lung, and other organ diseases. What is the essence of the operation? We have an absolutely non-functioning joint, the cartilage layer is worn out, everything is overgrown, it does not move.
How is osteoarthritis surgery done?
You then need to understand how the femur is arranged: it has a head that enters the joint and a trochanter to which many of the muscles that move the leg are attached. This is the skewer we feel through the skin. So during the surgery, the bone head is removed and the trochanter is left. Remains of cartilage are also removed from the cavity in the pelvic bone. The artificial head of the joint is replaced. The head "sits" on a metal rod that is attached to the femur. The incision is made in the inguinal region, with a length of only 7-8 cm.
The patient is lifted on the first day after surgery and forced to walk on the third day. And within a month or two, these patients will fully restore the range of motion of the joint. Of course, after such treatment of arthrosis, some motor treatment is required to contribute to healing. But that’s the doctor’s problem - to give expert advice, to teach you to use a new word of technique in your own body.
The dentures are made of lightweight and durable materials that make them durable. There are different types of prostheses. The doctor selects the optimal one based on the person's age, additional movement needs, and other factors. In Hungary, many such operations are performed completely free of charge. You have to stand in line for a while, but half a year is not a dozen years! And an endoprosthesis is performed. Today, thanks to advances in medicine, coxarthrosis can help you get rid of pain and lead an active lifestyle. The point is to see a doctor in time, because the more advanced the hip arthrosis, the more difficult it is to treat the patient, even with the help of modern technology.



















